Introduction
The European Union has taken a monumental step in regulating artificial intelligence with the introduction of the EU AI Act. As the world’s first comprehensive AI law, it sets strict compliance requirements for enterprises developing or deploying AI technologies.
The regulation aims to ensure that AI systems are trustworthy, transparent, and aligned with fundamental rights, fostering a harmonized market while mitigating potential risks. However, non-compliance could lead to hefty penalties up to 7% of global annual turnover.
For businesses leveraging AI, understanding the risk classification and compliance measures is crucial for ensuring regulatory alignment and avoiding financial repercussions.

Understanding the EU AI Act
What Is the EU AI Act?
The EU AI Act is a landmark regulation designed to govern AI usage across industries, ensuring ethical deployment and accountability. It applies to organizations that develop, use, or sell AI systems within the EU, regardless of their geographic location.
Key Objectives of the EU AI Act
- Promote AI innovation while minimizing risks
- Ensure fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI applications
- Prevent discrimination and misuse of AI technologies
- Protect fundamental rights and democratic values
Timeline for Implementation
- 2024: AI Act officially adopted
- 2025: Secondary legislation development and regulatory preparations
- 2026 (August): Full enforcement of the AI Act, with businesses expected to comply
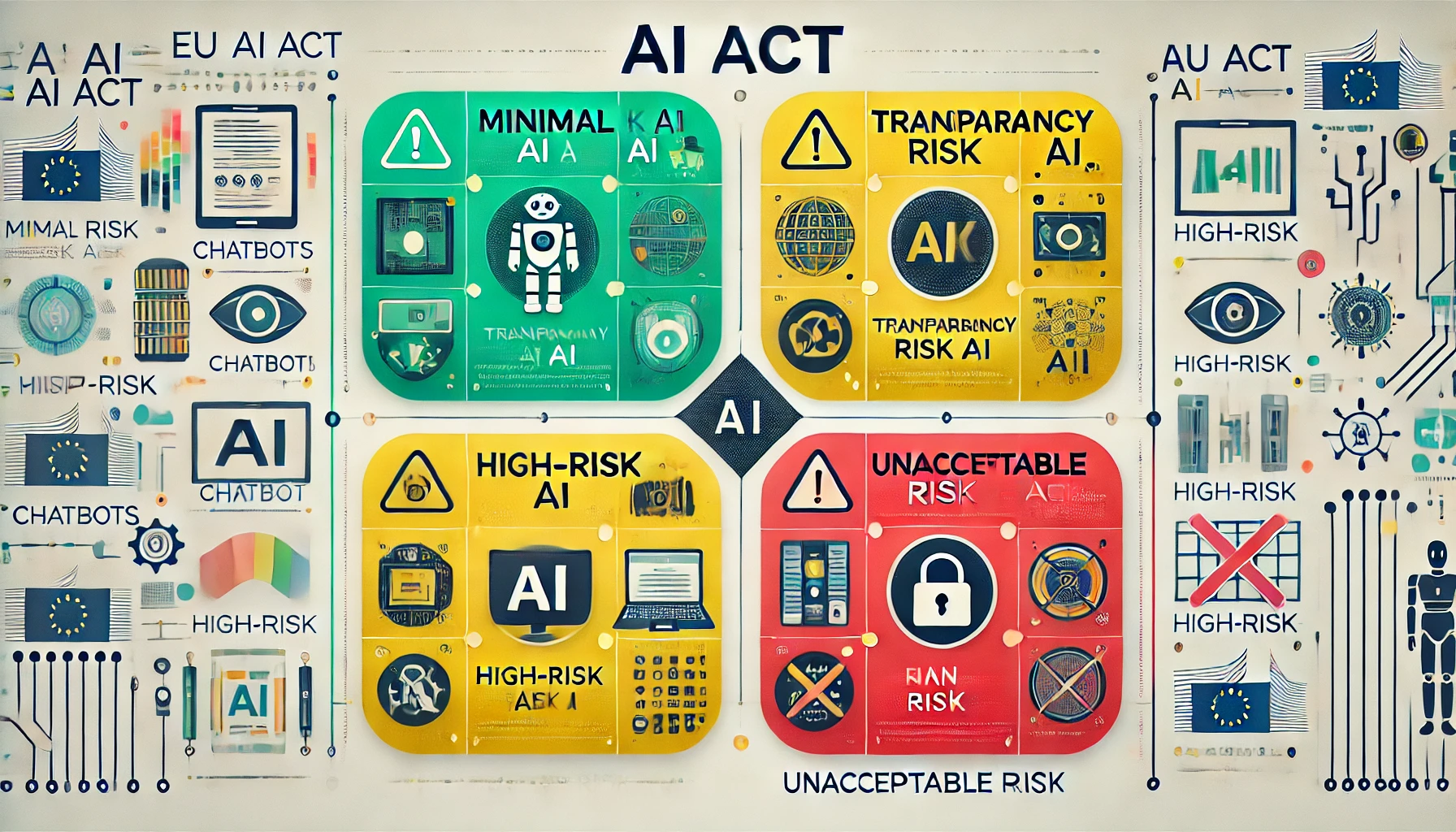
Key Classifications Under the EU AI Act
The EU AI Act categorizes AI systems into four risk levels, each with specific compliance requirements.
1. Minimal Risk AI
Examples:
- AI-powered chatbots
- Recommendation algorithms (e.g., Netflix, Spotify)
- Spam filters
🟢 Compliance Requirements: No mandatory obligations but businesses can voluntarily adopt best practices.
2. Specific Transparency Risk AI
Examples:
- AI-generated deep fakes
- Biometric categorization
- Emotion recognition technologies
🟠 Compliance Requirements: Businesses must clearly disclose AI-generated content and provide transparency on AI decisions.
3. High-Risk AI
Examples:
- AI in recruitment (hiring algorithms)
- Credit scoring and financial decision-making AI
- AI in healthcare (diagnostic tools, treatment recommendations)
- AI in law enforcement and border control
🔴 Compliance Requirements:
- Maintain extensive documentation and explainability reports
- Implement human oversight to prevent bias or errors
- Conduct continuous risk assessments and bias mitigation checks
- Strengthen cybersecurity measures to prevent AI exploitation
4. Unacceptable Risk AI (Banned)
Examples:
- AI for social scoring (e.g., ranking citizens based on behavior)
- AI that manipulates human behavior
- Predictive policing based on personal data
- Real-time biometric surveillance without consent
🚫 Compliance Requirements: Strictly prohibited in the EU market.
What Businesses Need to Do to Stay Compliant
1. Conduct an AI Risk Assessment
Enterprises must classify their AI systems based on the EU AI Act risk framework and identify potential compliance gaps.
2. Maintain Compliance Documentation
- Keep detailed records of AI model training, decision-making processes, and data sources.
- Ensure explainability in AI outputs and predictions.
3. Implement Human Oversight & Transparency
- Introduce human-in-the-loop monitoring for high-risk AI applications.
- Provide clear user notifications when interacting with AI systems.
4. Perform Bias & Data Quality Checks
- Use high-quality, unbiased datasets to train AI models.
- Conduct regular fairness audits to mitigate discrimination risks.
5. Engage in Regulatory Sandboxes & Testing
- Test AI models in controlled environments under regulatory supervision.
- Gather feedback and refine AI performance before full-scale deployment.
6. Partner with AI Compliance Consultants
- Seek expert guidance on legal complexities and compliance implementation.
- Conduct third-party audits to validate AI fairness and transparency.
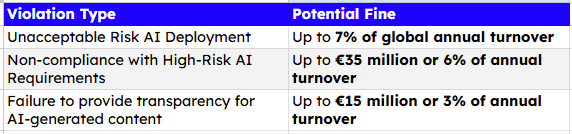
Potential Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with the EU AI Act could result in severe penalties:
How Nyx Wolves Can Help
Navigating the EU AI Act can be complex, but Nyx Wolves specializes in AI development and compliance consulting to help businesses stay ahead. Our services include:
- AI Risk Classification & Compliance Audits
- Bias Detection & Model Fairness Assessments
- AI Documentation & Regulatory Reporting
- Human-Centric AI Implementation Strategies
- Secure AI Infrastructure for High-Risk AI Systems
By partnering with Nyx Wolves, enterprises can ensure that their AI solutions are both innovative and fully compliant, avoiding costly penalties while maintaining a competitive edge.
Conclusion: Preparing for 2026 and Beyond
With the AI Act’s key provisions taking effect in August 2026, businesses must start preparing now. AI-driven enterprises need to evaluate their risk exposure, implement compliance measures, and partner with AI governance experts to future-proof their operations.
🚀 Is your AI strategy aligned with the new regulations? Let’s discuss how Nyx Wolves can help you navigate the evolving AI regulatory landscape. Contact us today to ensure compliance with the EU AI Act!
FAQs
The EU AI Act is a regulatory framework designed to govern AI usage in the EU, ensuring ethical AI development and preventing potential risks.
Any company that provides AI solutions in the EU regardless of where they are based must comply with the law.
Industries like finance, healthcare, recruitment, and law enforcement face the strictest compliance requirements.
Companies should classify their AI systems based on risk levels and document their compliance strategies accordingly.
Full enforcement begins in August 2026, but businesses should start their compliance preparations immediately.